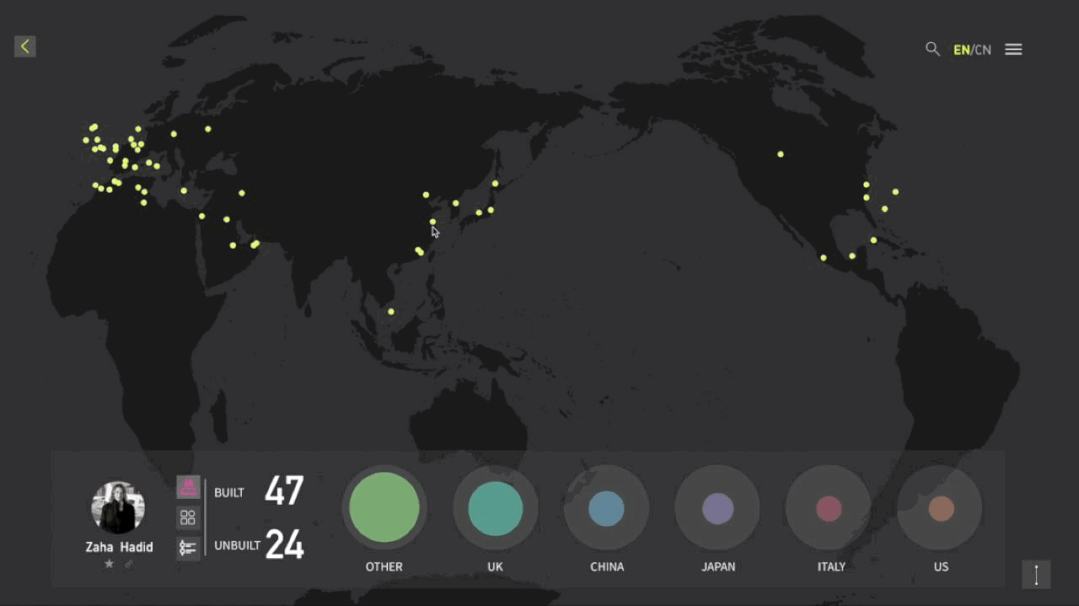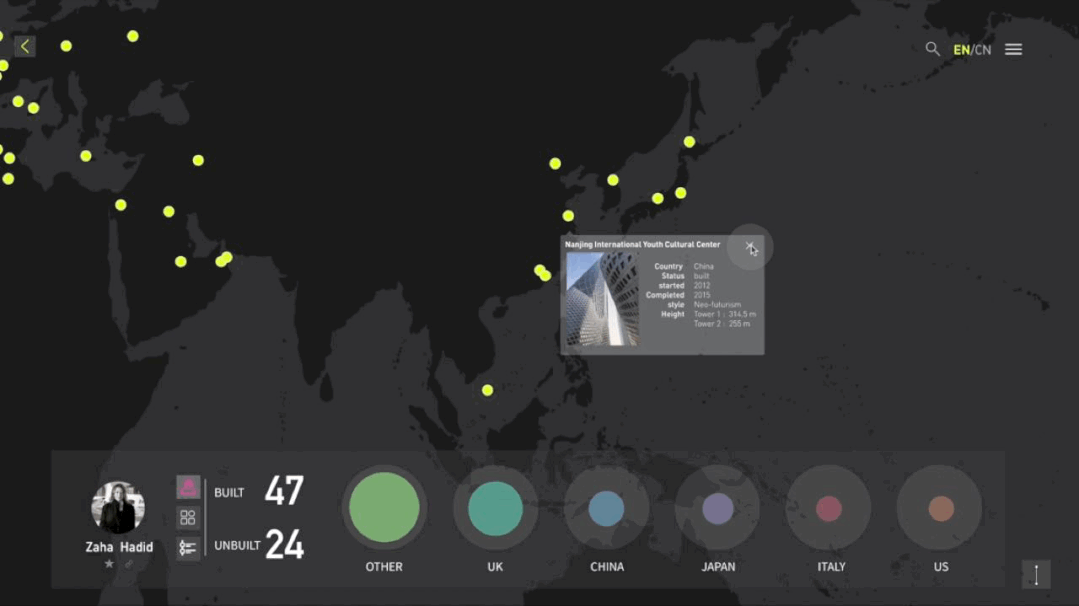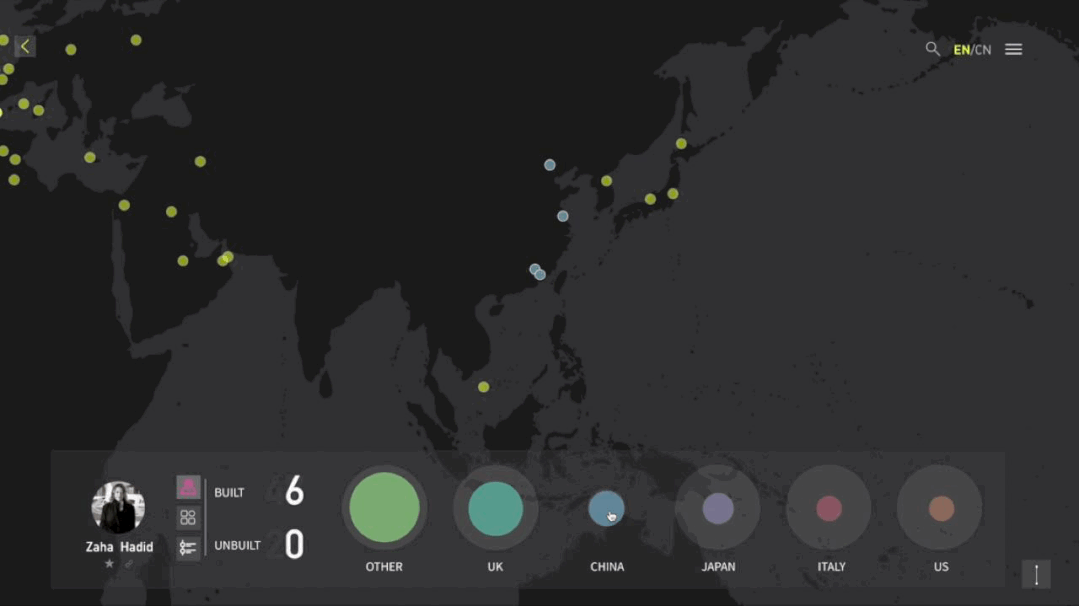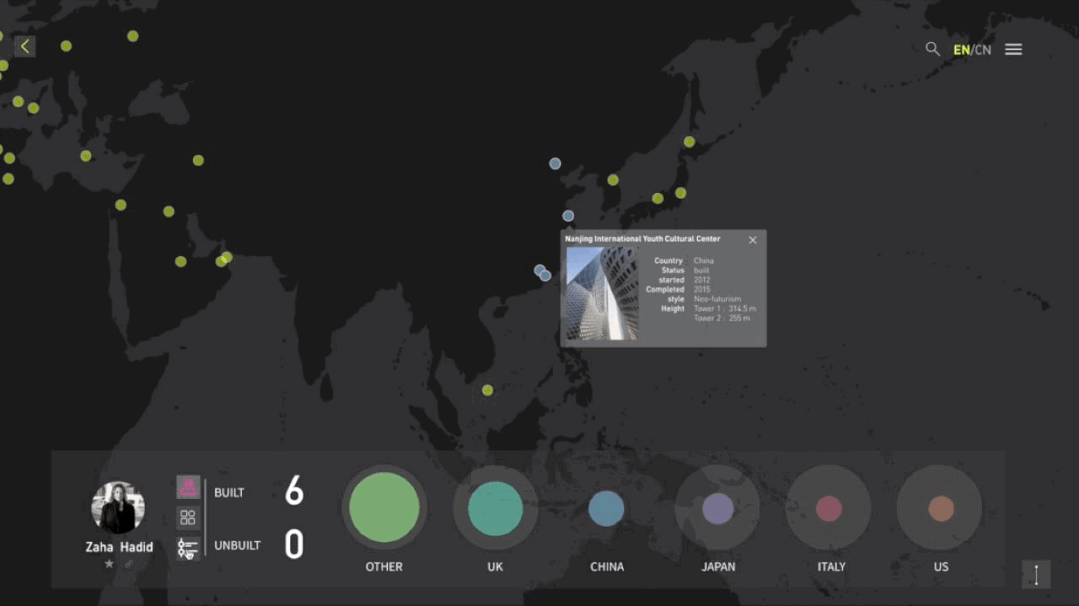
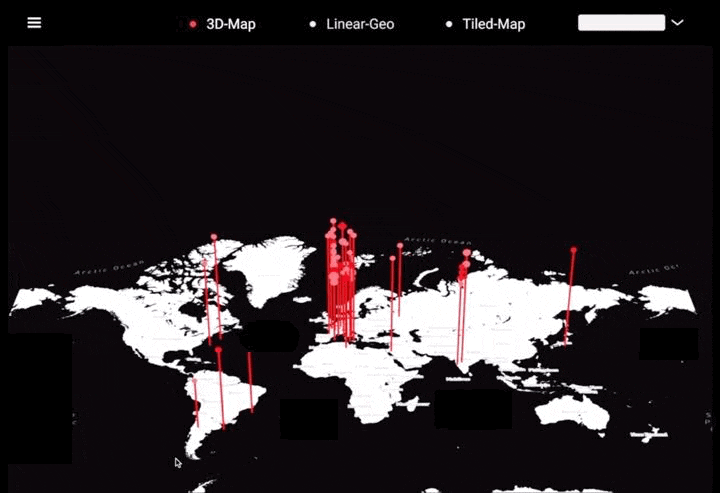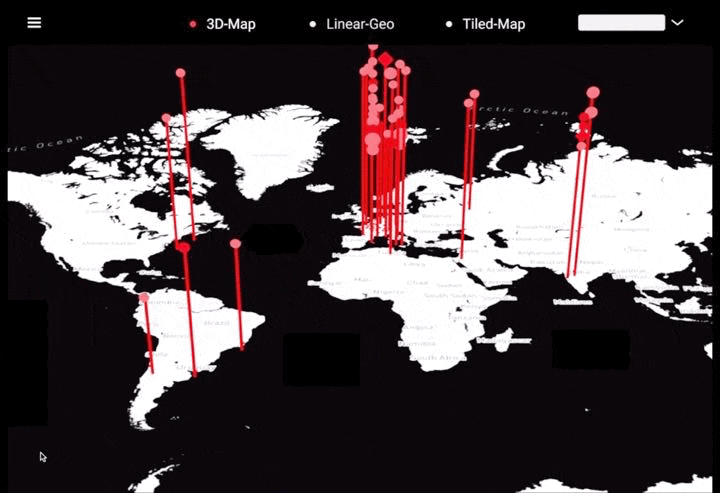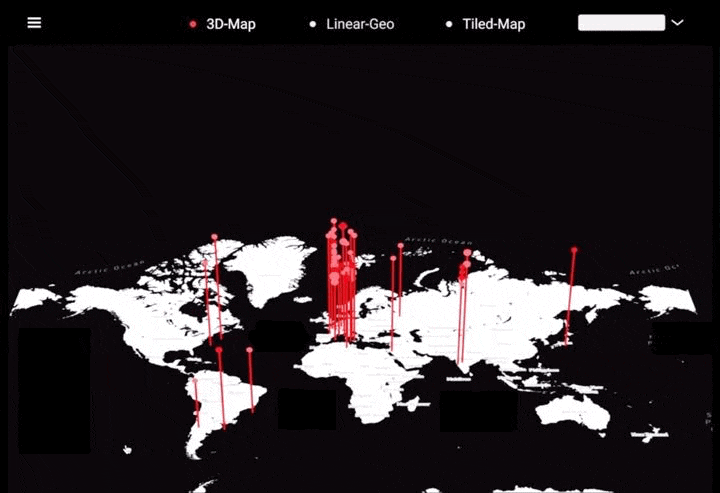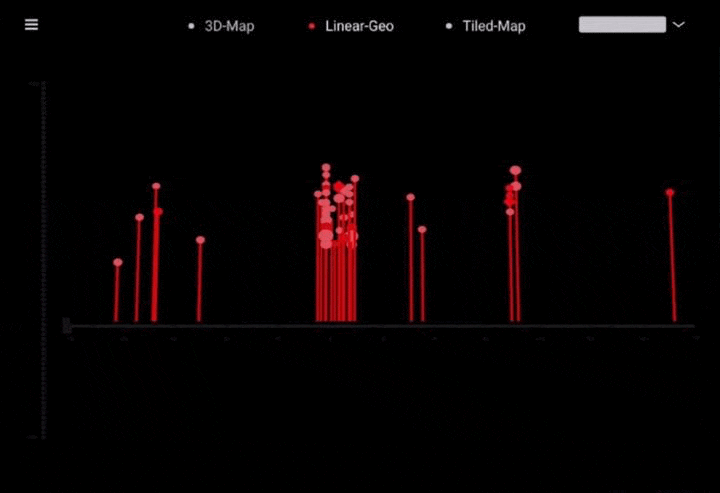
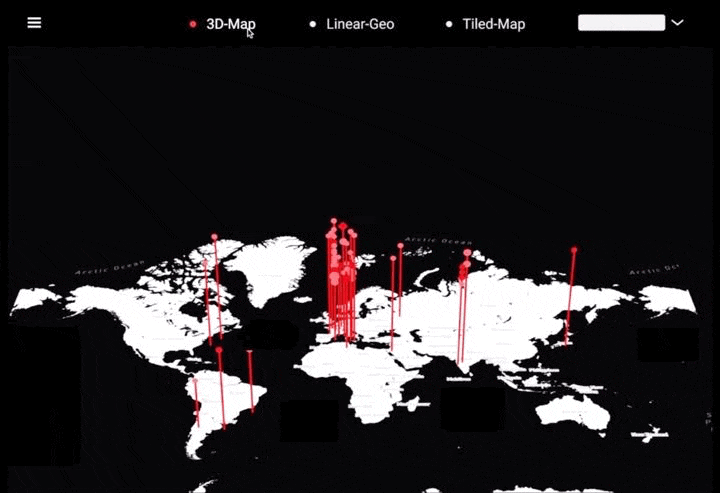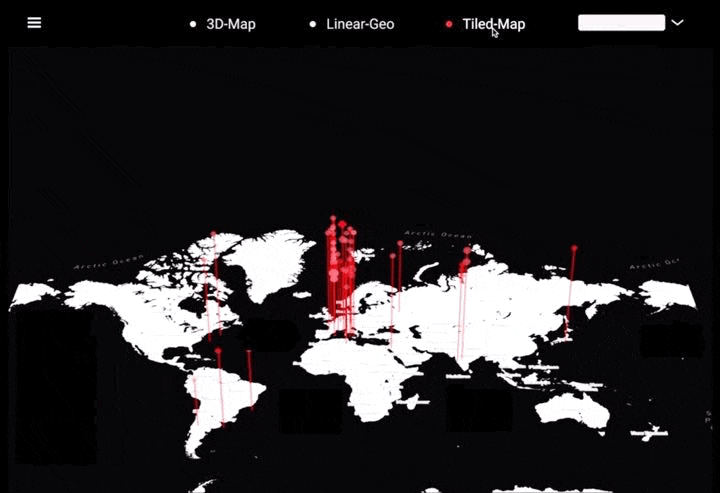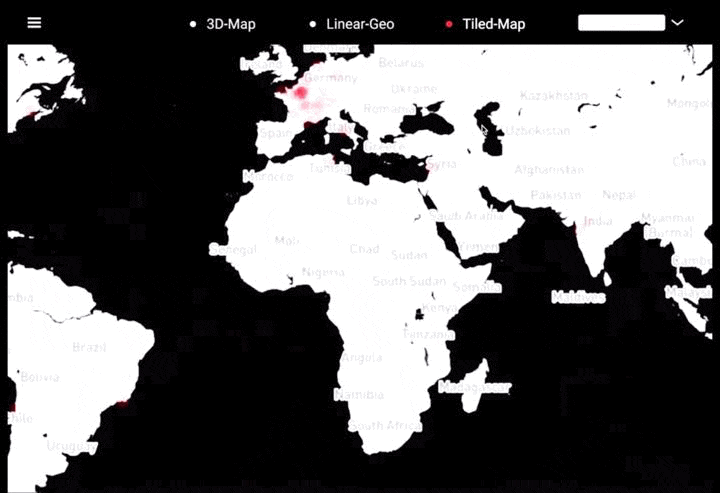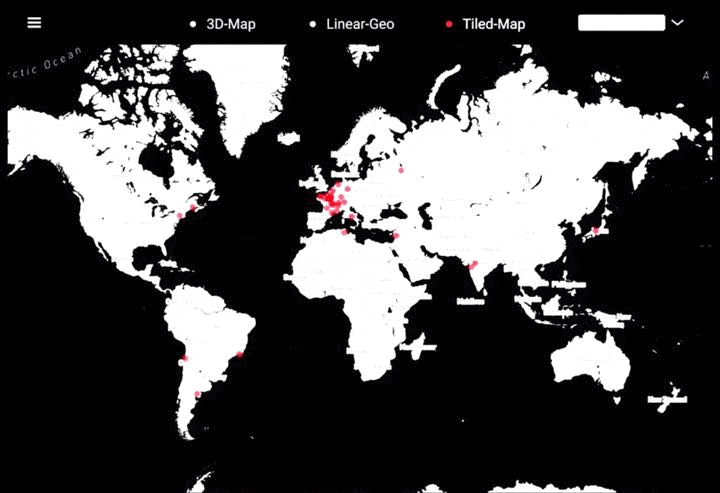
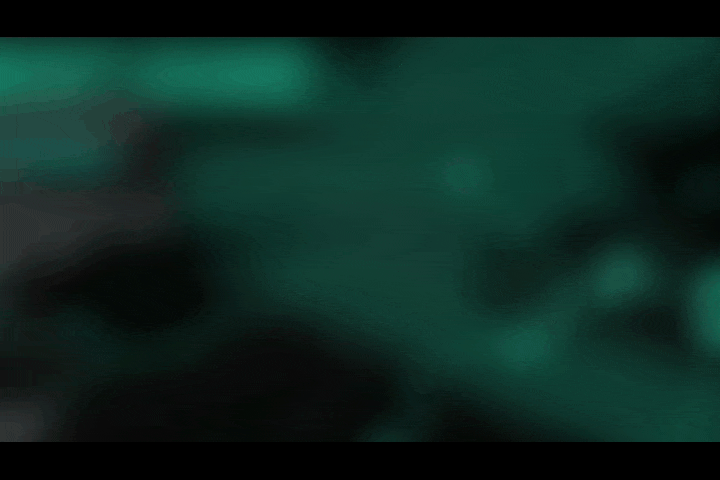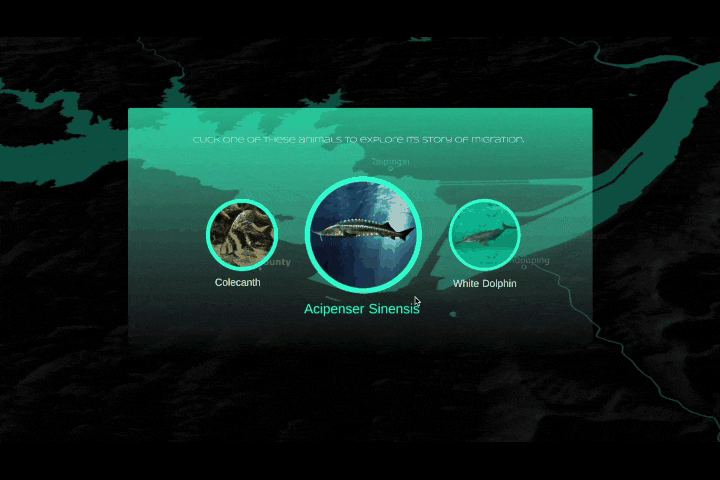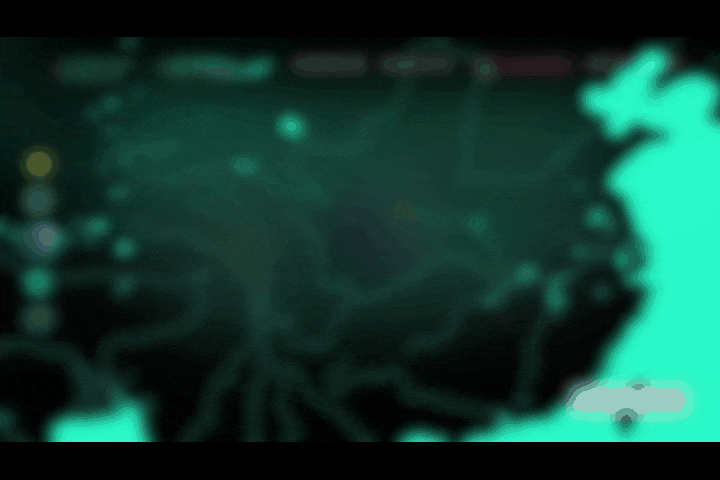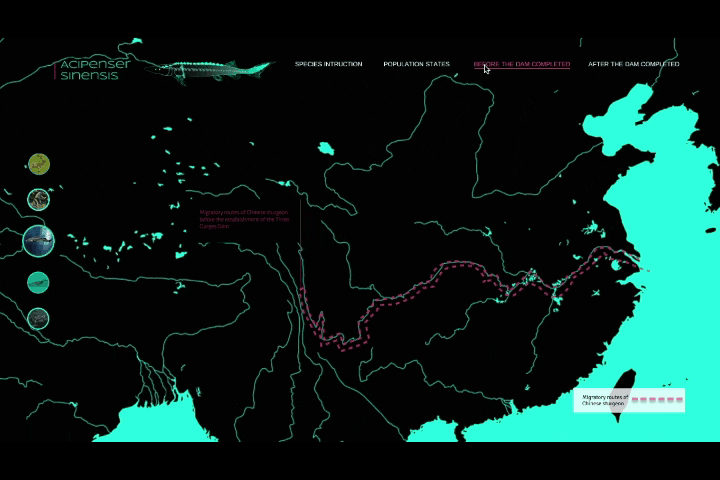工作坊作品集锦
随着通信和网络技术的浪潮式发展,海量数据在不断生成。数据正在成为人类社会的重要资产和基础设施,蕴含着无限价值。而随着人机交互范式的迭代式更新,管理、生产和消费数据的方式也在持续涌现,一个在跨领域语境下信息相互交融和影响的社会图景正在生成。设计师,作为提出问题、解决问题以及总是试图改善和改变他们周围的世界的实践家,源源不断地为世界提供良性干预,因而在这个图景中扮演着越来越重要的角色。在这种干预中,数据技术和信息可视化已经成为我们的有力工具:去追踪、采集、表现、感知、反思、助益人与世界的关系,塑造故事,探索未知。With the wave-like development of communication and network technologies, huge amount of data is being generated continuously. Data is becoming a critical asset and infrastructure for human society, containing infinite value. And with the iterative renewal of the human-computer interaction paradigm, ways to manage, produce and consume data are emerging, creating a social landscape where information intersects in a cross-domain context. Designers, as practitioners who ask questions, solve problems and always try to improve the world around them, play an increasingly important role in this picture by providing a constant stream of beneficial interventions in the world. In this intervention, data technology and information visualization have become powerful tools for us: to track, capture, represent, perceive, reflect on, and contribute to the relationship between people and the world, to shape stories, and to explore the unknown.

左右滑动查看更多

左右滑动查看更多

左右滑动查看更多

左右滑动查看更多

左右滑动查看更多

左右滑动查看更多

左右滑动查看更多

左右滑动查看更多
总目标
探索同一文本内容在“平面”和“交互”两种设计框架下的不同形态。使用交互技术和可视化方法,调和有限的媒介空间与无限的数据量之间的矛盾,把传达的信息从一次大量转变为多次大量,把受众从被动的浏览者转化为主动的体验者。
了解数据驱动的可视化设计工作流,利用迭代周期进行设计和开发实践:- 基于观察和假设,提出问题、进行调研、形成方案,迭代式地完善和实现设计概念;
- 形成对数据结构的基本认知,了解从后端到前端的数据可视化工作流;
- 使用交互设计的思维重新审视以信息/数据为对象的视觉传达设计;
对现代信息可视化方法的历史背景、特性、功能使命有基础的认知:- 从分类学视角熟悉可视化中人类感知、交互空间、交互技术的概念及应用;
- 了解可视化作为一种信息的编码、传播和分析技术,以及任务驱动信息可视化人机界面设计方法;
- 能够通过展示和讨论,分析和评价信息可视化的内容、形式和交互性,展示协作能力;
在视觉传达设计的框架下,实现基于数据的体验,构建具有建设性的设计对话:- 能够制作可交互原型,清晰地展示设计想法、表达设计观点;
- 能够使用编程语言,创建简单的基于 Web 的可视化图形、图表和地图;
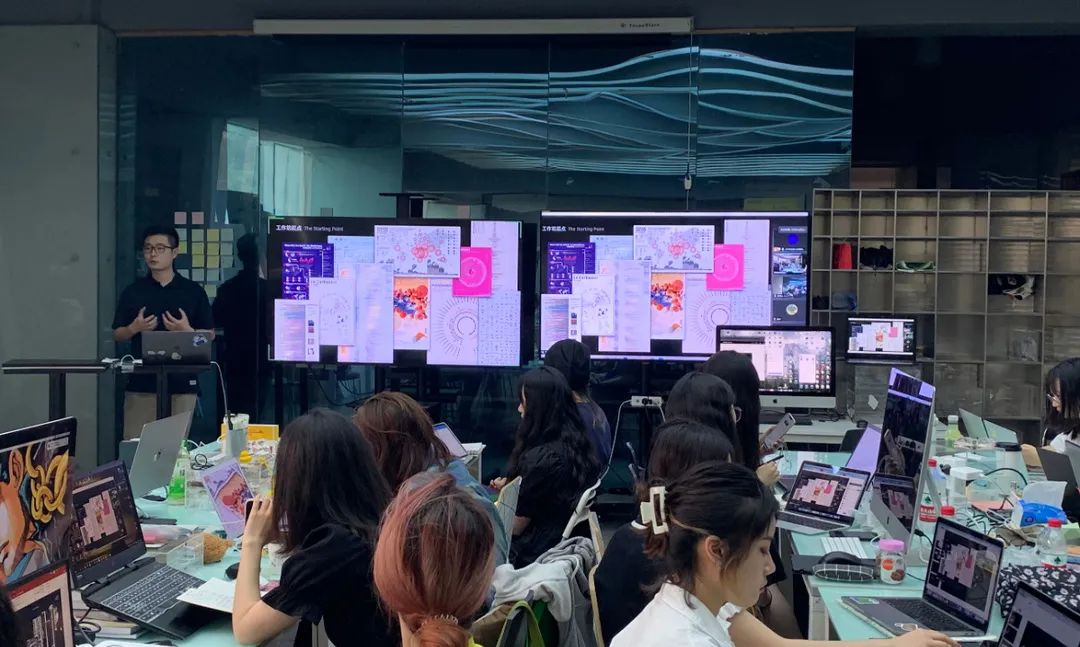
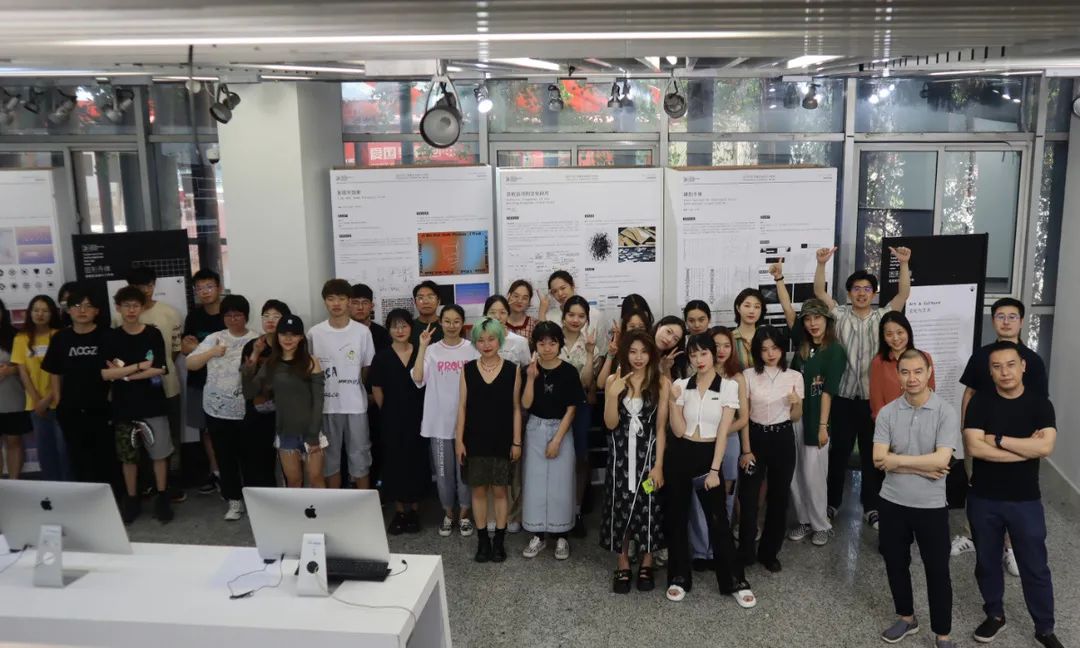
本次工作坊以「图形升维」为主题,为视传背景的学生量身定制教学内容:引入可视化和人机交互的学科视角;在视觉传达的框架和协同设计的实践中,帮助学生理解数据结构和视觉编码的基本概念和原理、感受不同媒介形式的传播特点和差异、重新审视既有的信息图作品、创建数据驱动的人机界面,从而表现设计的价值主张。设计学院信息设计专业的大三本科生、大四毕业生、研究生等21名同学全程参与了本次工作坊。在本次工作坊中,他们的足迹遍及了缤纷的学科版图。他们一起上课研讨、进行协作式的阅读分享、从大规模案例分析中分享见解和萃取经验、利用自总结的分析框架和设计空间来助益设计实践、互相进行有建设性的作品评议、参与有成长性的小组合作…… 他们站在扎实的平面信息设计的基础上,在极短的时间内,穿越了无数的知识荆棘,初窥了数据驱动的可视化的样貌,实现了令人兴奋和着迷的阶段性成就。

微观教学模块
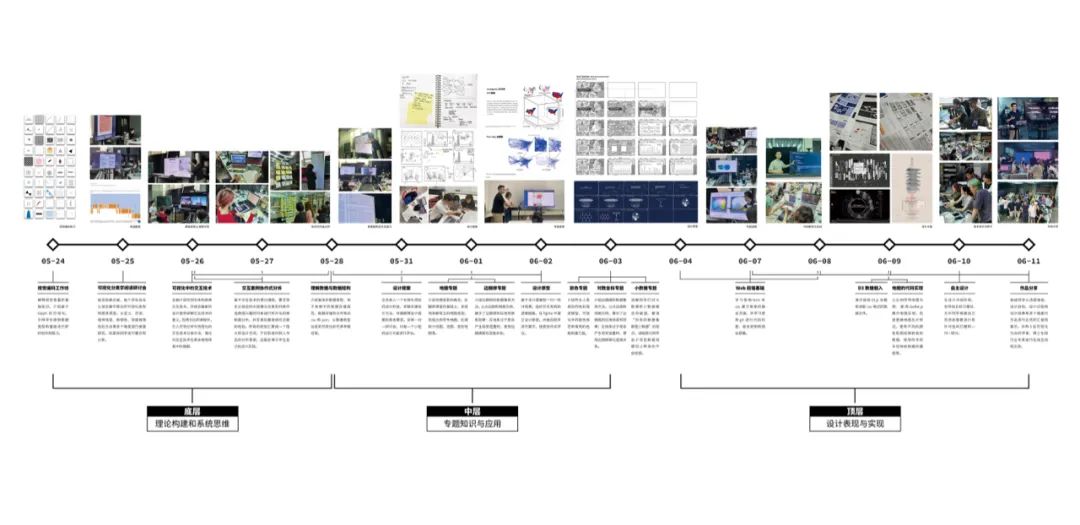
工作坊教学过程
6月11日,工作坊还组织了作品分享会,并进行了线上同步直播,共吸引了176名在线观众。15个小组现场演示了信息交互设计作品,回顾了作品的选题缘起、设计过程和可视化方法,并获得了领域内5名专业嘉宾的一对一点评。嘉宾们从探索空间、数据操纵、跨学科合作、地图信息增强、情感化设计、数据驱动叙事、个人化数据等多个角度提出了大量宝贵建议。
点评嘉宾
谢李文含
香港科技大学可视化与人机交互方向博士生
蓝星宇
同济大学智能大数据可视化实验室博士生
陆旻
深圳大学建筑与城市规划学院助理教授
陈昱凝
英国帝国理工大学 & 皇家艺术学院创新设计工程双硕士
罗锦妮
阿里巴巴集团数据技术和产品部体验设计专家
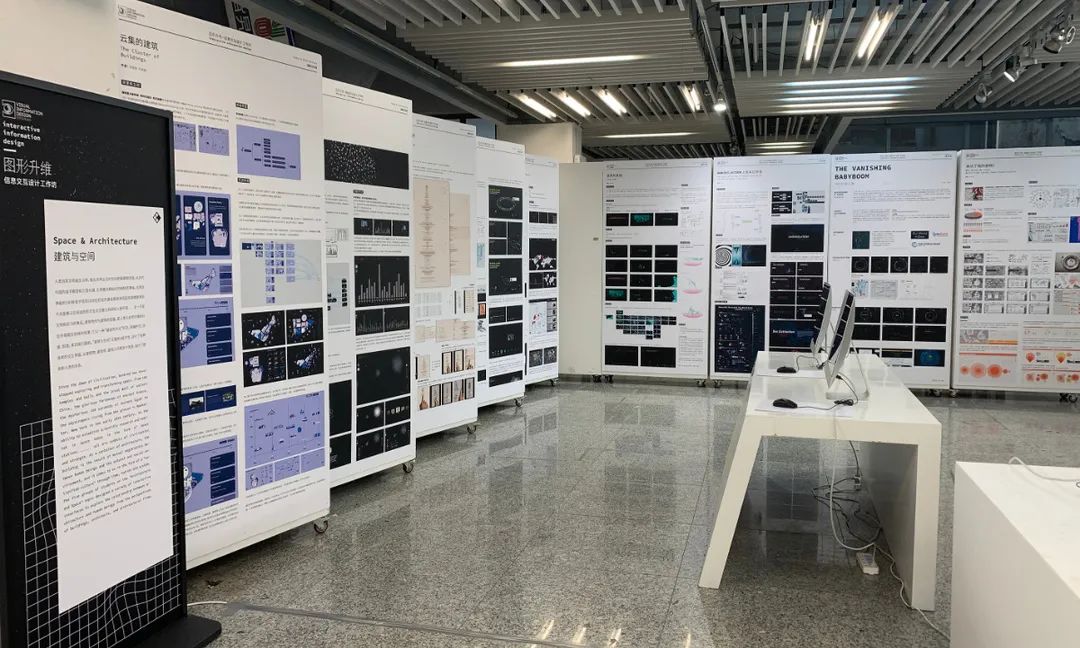
学生通过自由探索,生成了四大精彩议题 — 建筑与空间、人类与未来、文化与艺术、网络与生活 — 处处体现着对文明的向往、对社会的思辨以及对人类的关怀。他们的作品综合运用了各种设计方法和交互技术,涉猎了数据展示和叙事、探索和分析等多个方向,在人机界面上建立了对时间和空间的映射、以数据驱动的思维形成了解释性文本、通过图形化的手段对其进行了修饰和增强,从而能够从可持续的视角在不同的文化维度上建立弹性的对话空间。
文化与艺术 Art & Culture
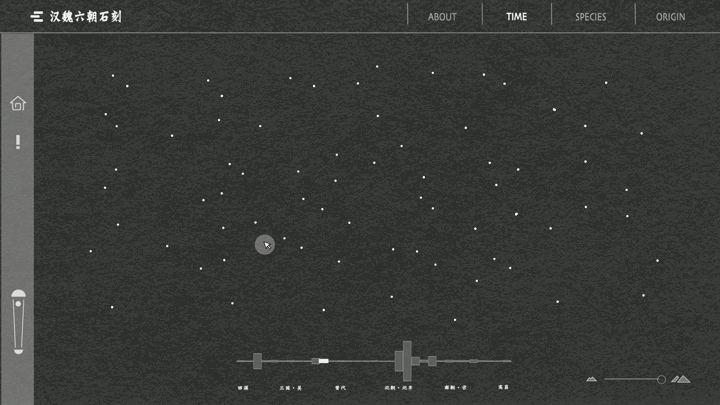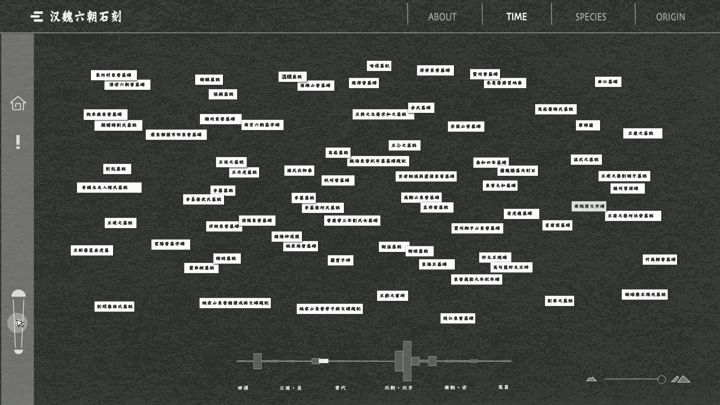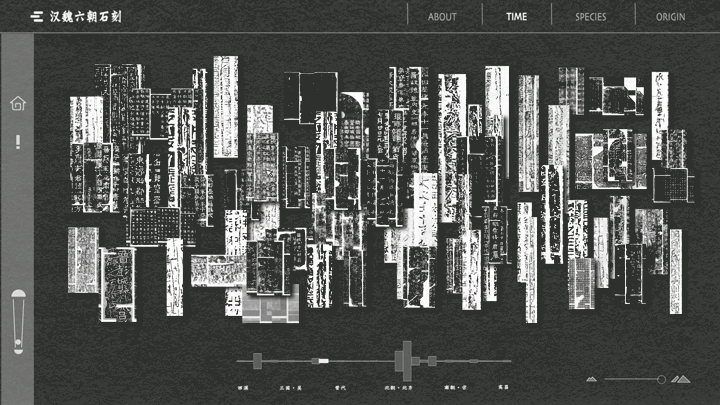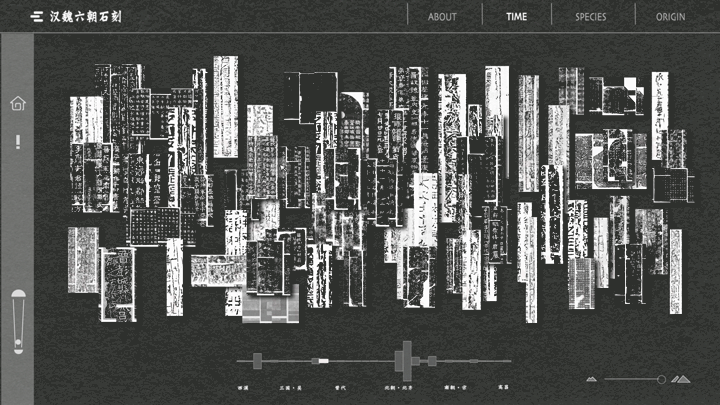
一提起“文化”,我们总是思维定势般地把它和“传统”联系在一起。没错,文化的产生、演化和传播需要经历漫长的过程,这决定了很多文化必然是“传承”的和“传统”的。但随着数字技术的参与式发展,我们的文化的传播形态不再局限于印刷物等平面静态媒介,得以突破禁锢、穿越时空、焕发生机。“文化与艺术”议题的3组学生使用批判性的视角、修辞学的方法、数字化的手段,记录、重组、再现了中国古代碑刻文化、基于京杭大运河的空间文化以及毕加索绘画艺术,并且通过交互技术进行了线上布展,创造了动态环境和超越平面媒介的文化体验。
When we talk about "culture", we always associate it with "tradition" in a stereotypical way. Yes, culture takes a long time to emerge, evolve and spread, which means that many cultures are necessarily "inherited" and "traditional". However, with the participatory development of digital technology, the form of communication of our culture is no longer limited to print and other static media, but has been able to break through the confines, travel through time and space, and come to life. Using critical perspectives, rhetorical methods, and digital means, the three groups of students in "Art and Culture" documented, reorganized, and recreated ancient Chinese inscription culture, spatial culture based on the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal, and Picasso's paintings, and used interactive technology to curate online exhibitions, create dynamic environments and cultural experiences that go beyond flat media.


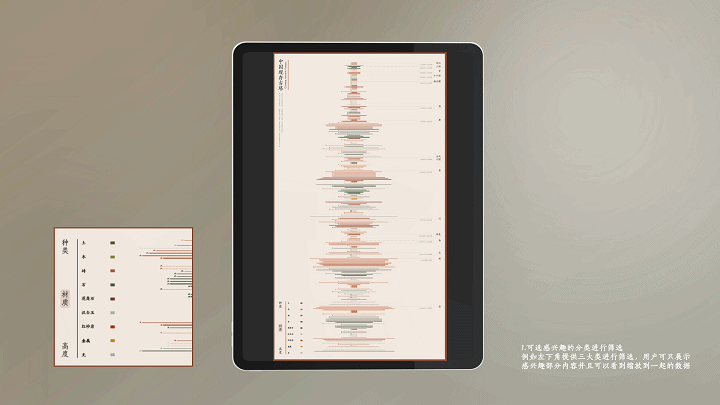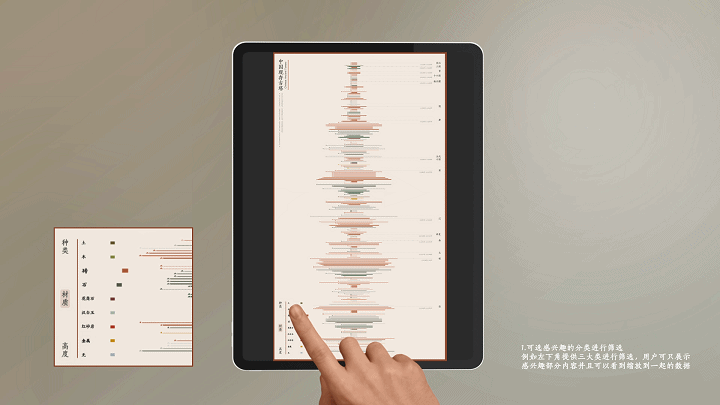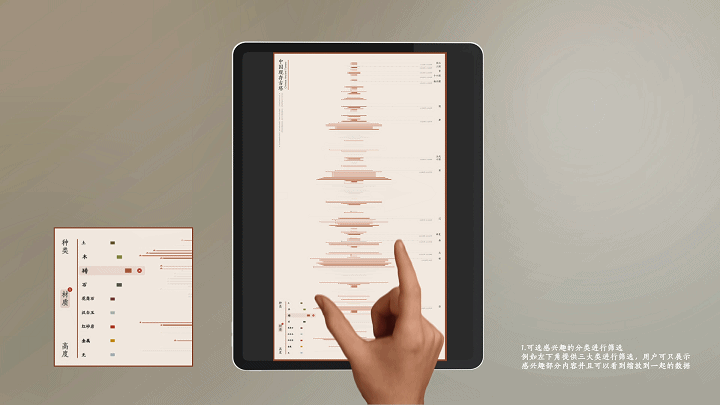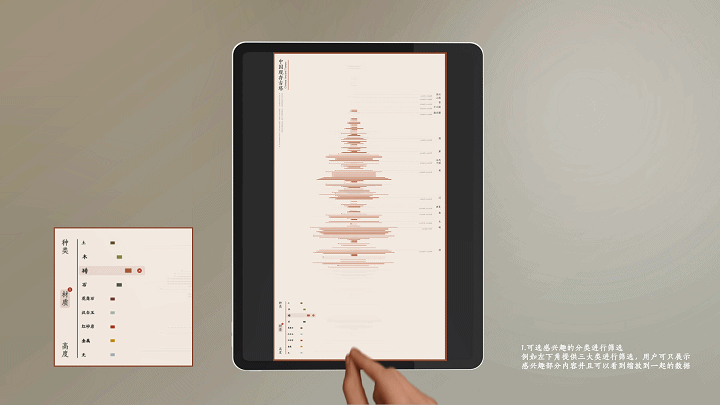
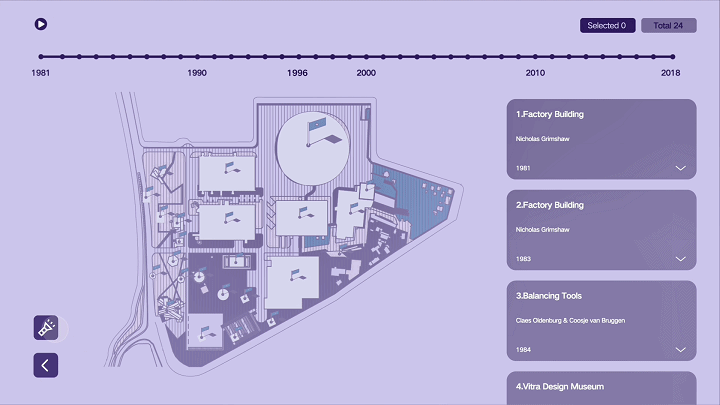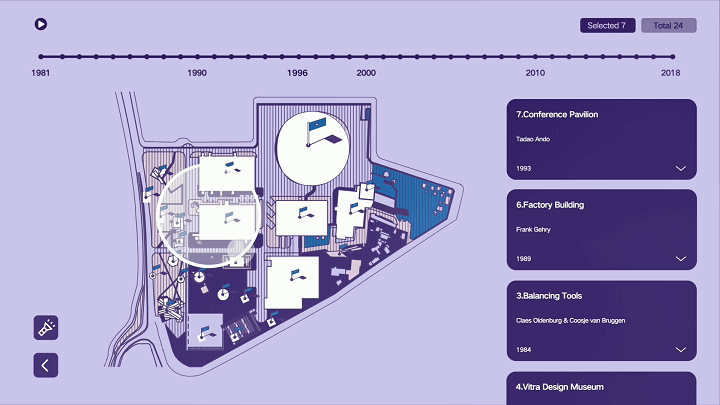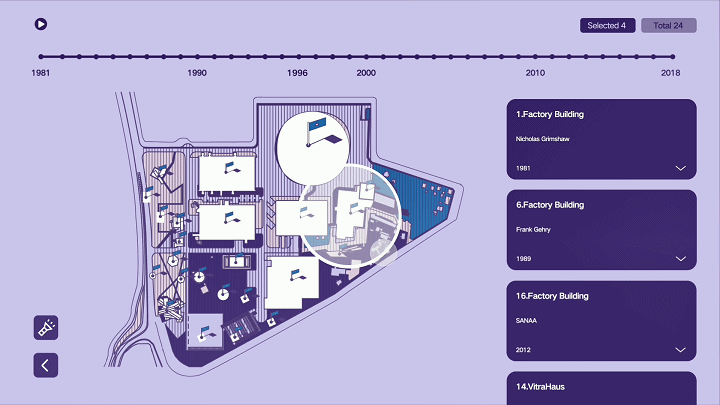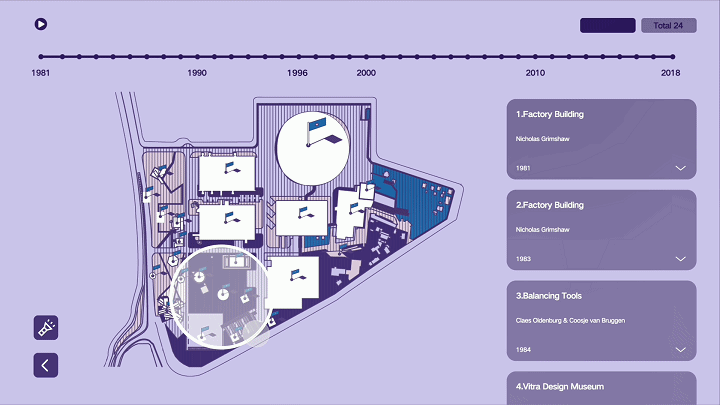
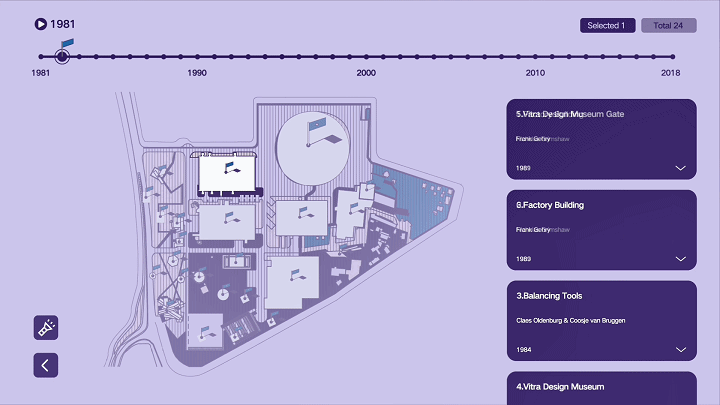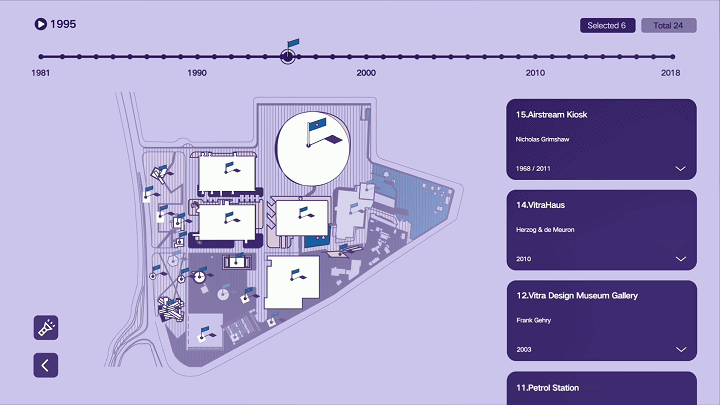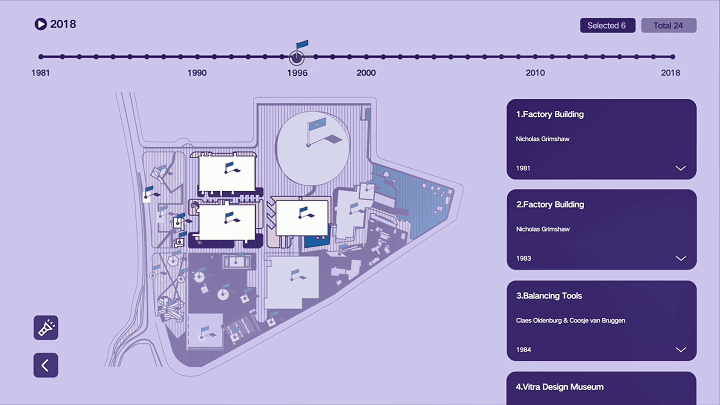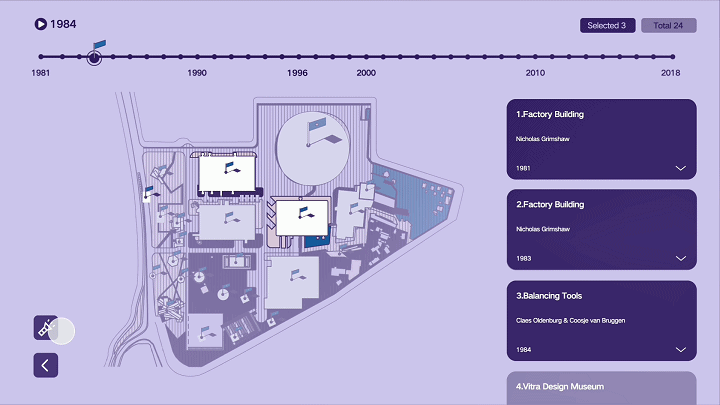
建筑与空间 Space & Architecture
人类自其文明诞生以来,就从未停止过对空间的探索和改造。从古代中国的庙宇殿堂和万里长城、古希腊光辉灿烂的帕特农神庙、古埃及神秘的140座金字塔到20世纪初纽约曼哈顿拔地而起的高楼群再到今天能够以空间站的形式在太空建立科研和人居环境……无一不是文明和实力的象征。建筑物作为建筑的容器,是人类与自然环境和社会环境相互协商的结果,它以一种“凝固的文化”形态,穿越时代、民族、制度,来到我们面前。“建筑与空间”议题的5组学生,设计了各种各样的交互界面,从建筑物、建筑师、建筑公司等多个角度,探讨了建筑和人类的关系。Since the dawn of civilization, mankind has never stopped exploring and transforming space. From the temples and halls and the Great Wall of ancient China, the glorious Parthenon of ancient Greece, the mysterious 140 pyramids of ancient Egypt to the skyscrapers rising from the ground in Manhattan, New York in the early 20th century, to the ability to establish scientific research and habitat in space today in the form of space stations ...... all are symbols of civilization and strength. As a container of architecture, the building is the result of mutual negotiation between human beings and the natural and social environment, and it comes to us in the form of a "solidified culture" through time, nation and system. The five groups of students on the "Architecture and Space" topic designed a variety of interactive interfaces to explore the relationship between architecture and human beings from the perspectives of buildings, architects, and architectural firms.




左右滑动查看更多
左右滑动查看更多
人类与未来 The Future of Humanity
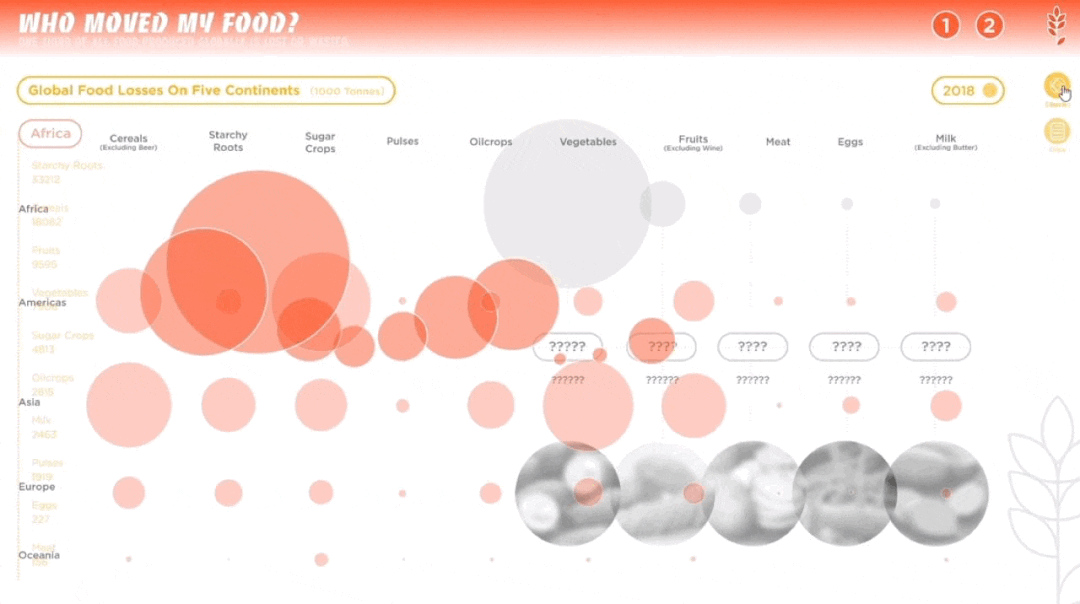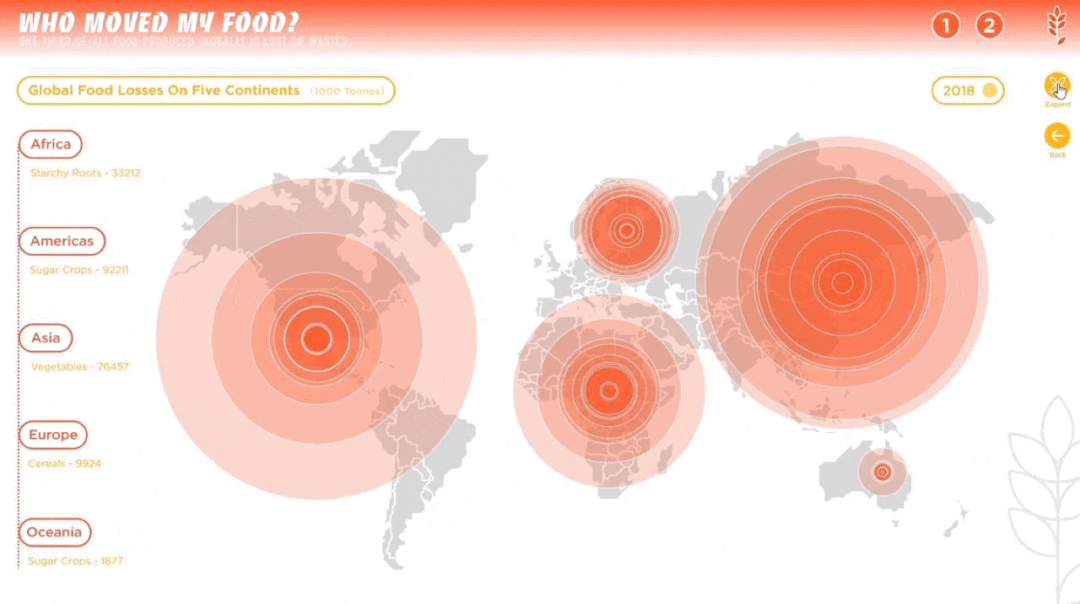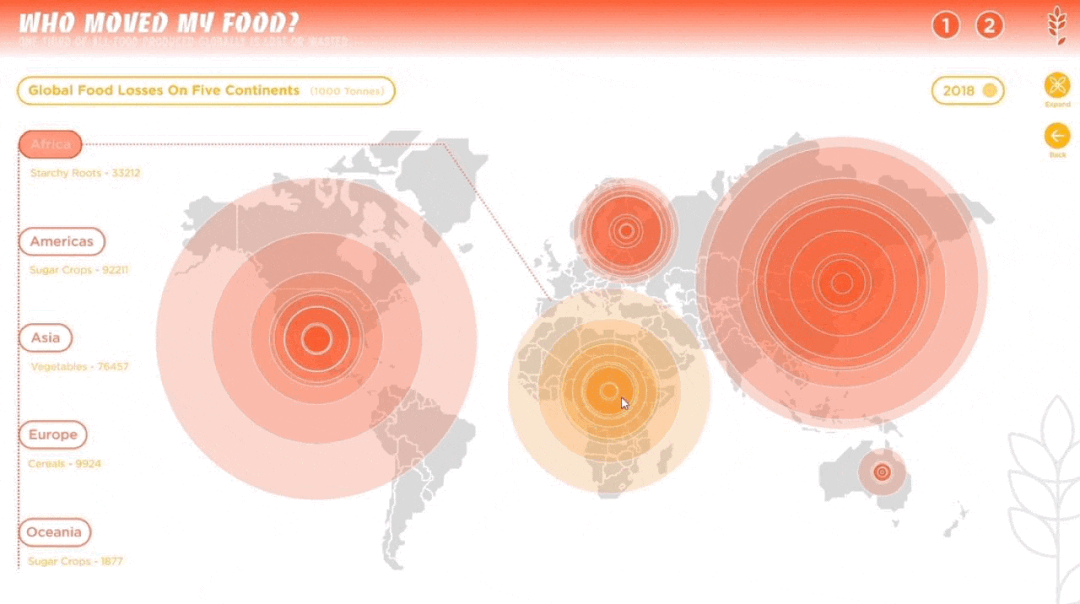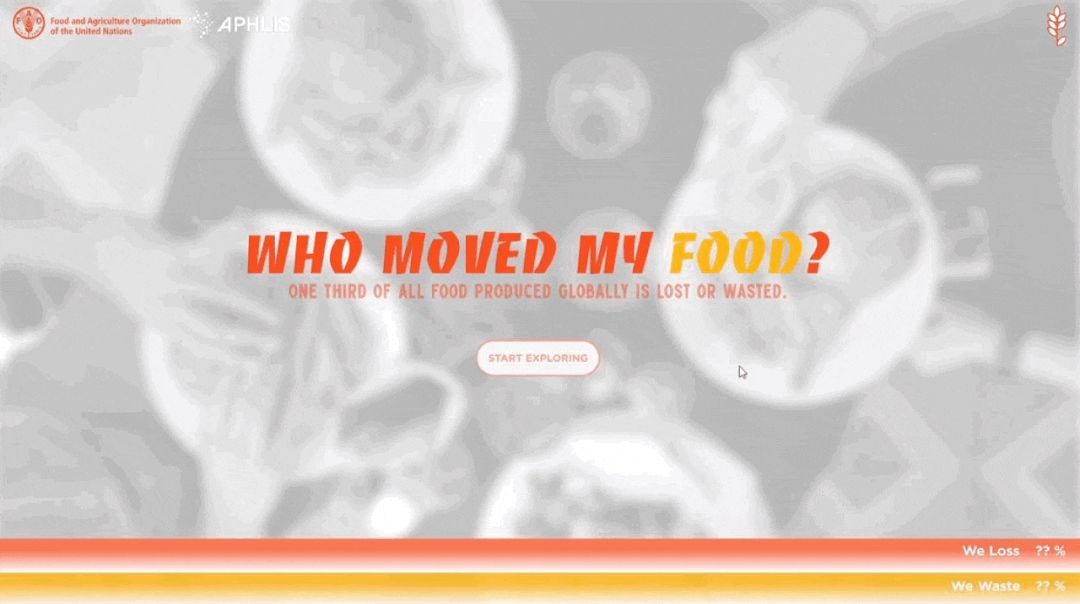
人类作为这个星球暂时的所谓“主宰”,一直在试图改造、支配和控制世界,随之而来的还有肆意妄为的破坏、消亡和毁灭。人类文化的复杂性和多样性决定了人类并不总是“团结”的,人类擅长为自己添加制衡——没有约束,就制定法律;有人破坏,就有人保护。一部分有识之士,一直在学习如何更好地与环境共生、与其他物种共存,从联合国17个可持续发展目标,到中国为消除贫困、改善公共健康、对抗气候变化作出的负责任的努力,都让我们看到一个广泛、深刻、有韧性的人与自然互动图景正在生成。这一议题的4组学生,从人口、人类工程与生物多样性、人类社会危机、粮食浪费与粮食安全等多个角度切入,探讨人与人、人与自然、人与社会的恒久关系。As the temporary "masters" of the planet, humans have been seeking to transform, dominate and control the world, and with it, to wreak havoc, extinction and destruction. The complexity and diversity of human culture has determined that humans are not always "united" and that they are good at adding checks and balances to themselves -- if there are no constraints, laws are made; if there is destruction, there is protection. From the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals to China's responsible efforts to eradicate poverty, improve public health, and combat climate change, we see a broad, deep, and resilient picture of human-nature interactions in the making. The four groups of students on this topic cut through the perspectives of population, human engineering and biodiversity, human social crisis, and food waste and food security to explore the constant relationship between people, nature and society.

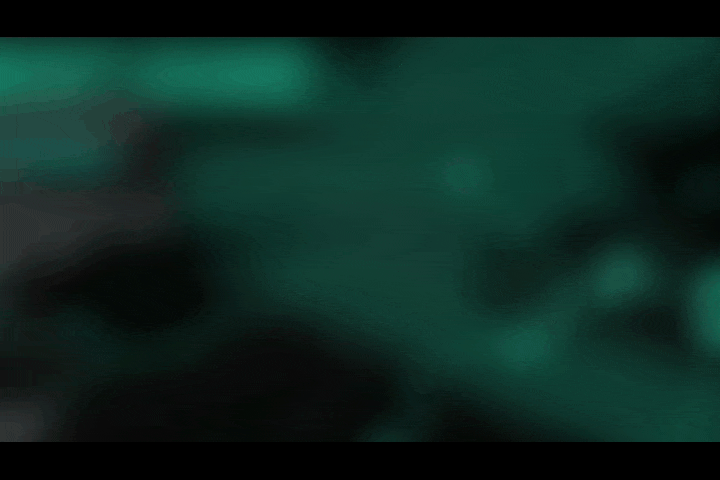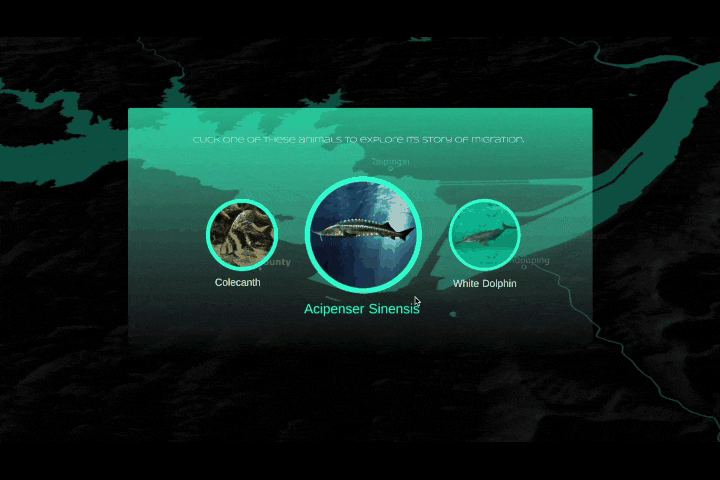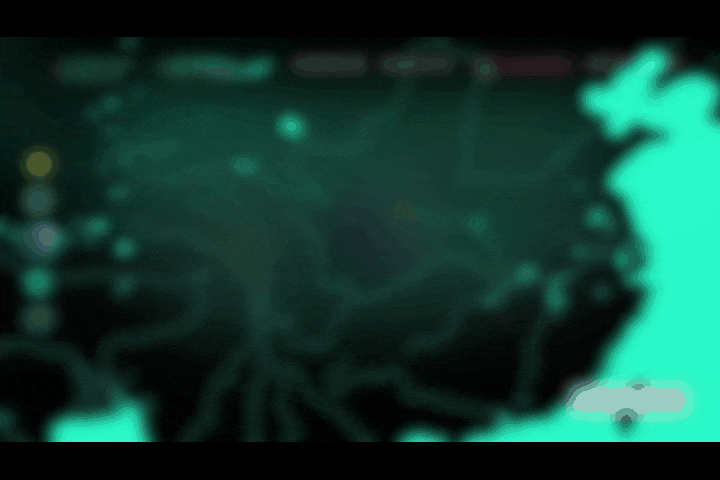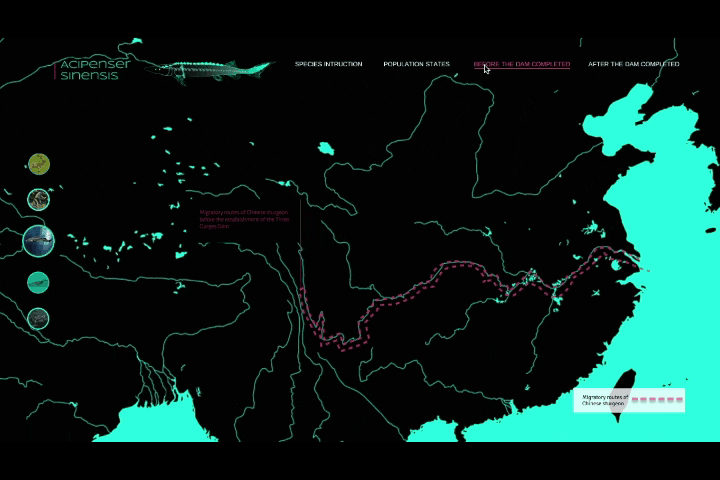


左右滑动查看更多
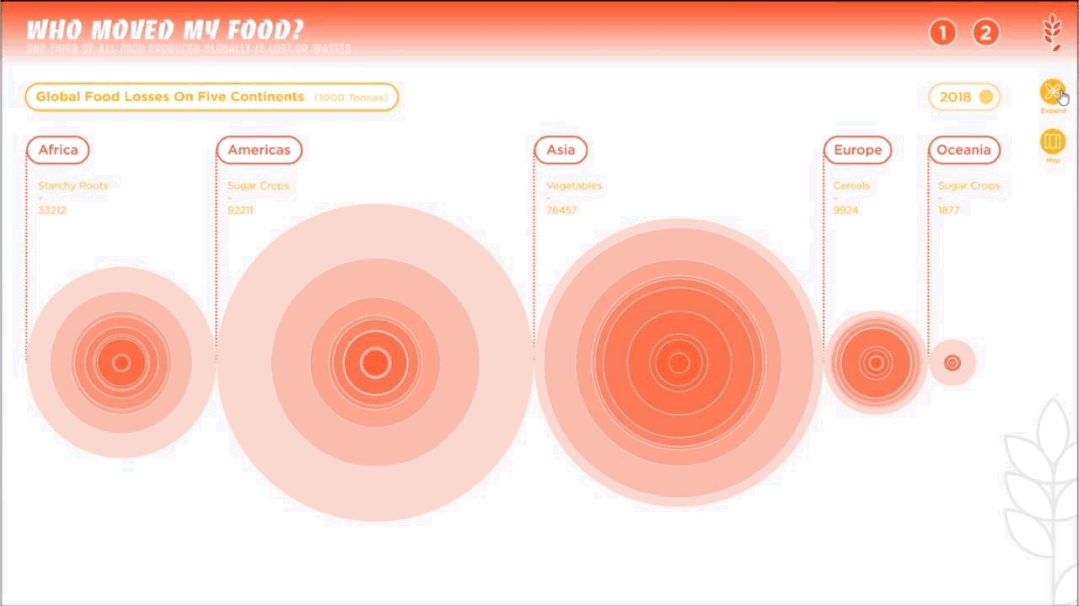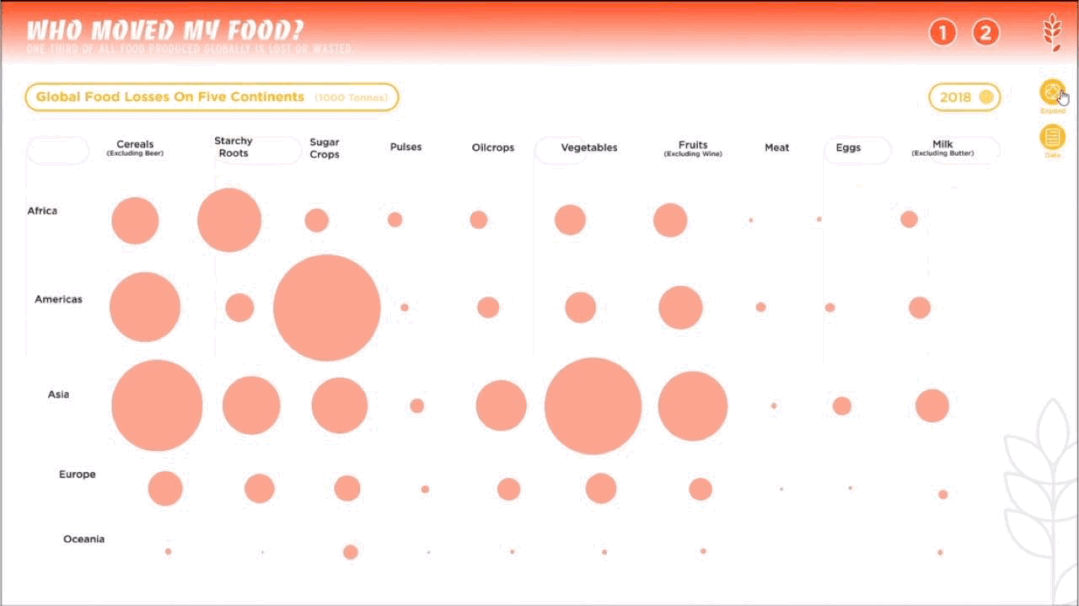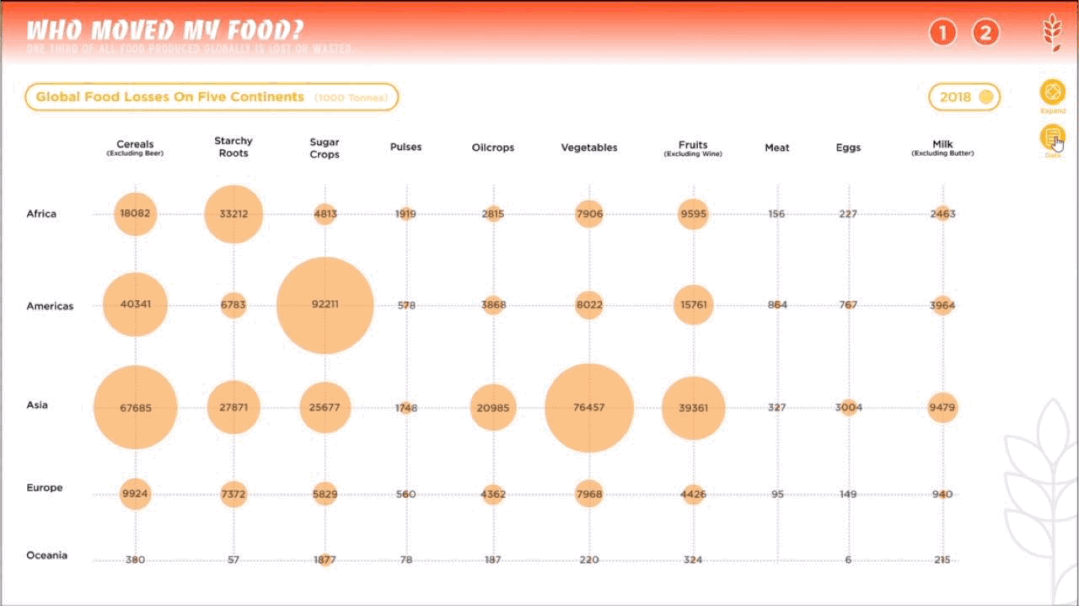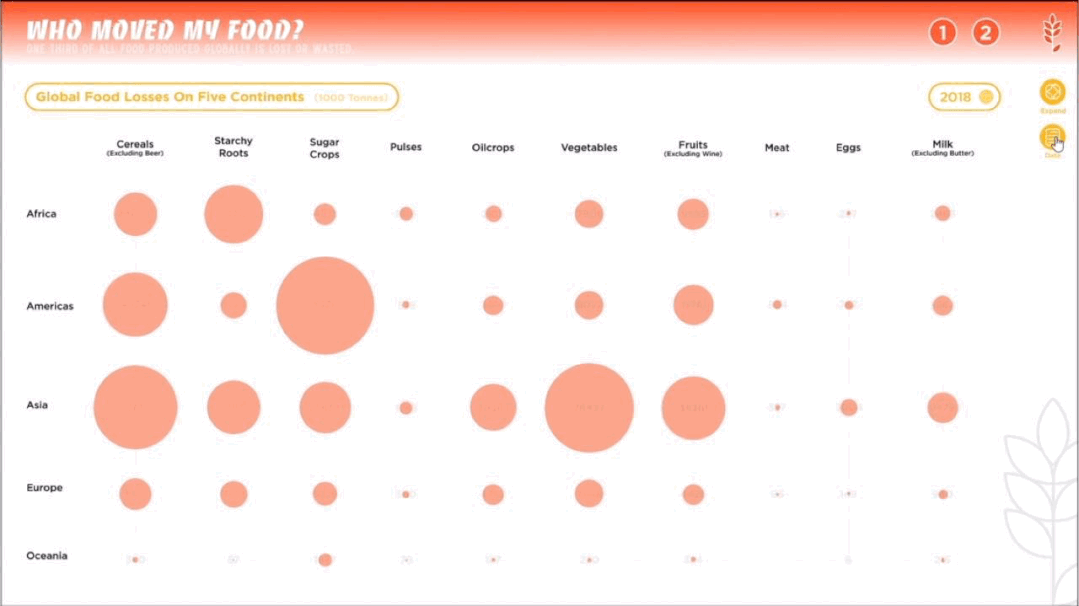
左右滑动查看更多
网络与生活 Network & Daily Life
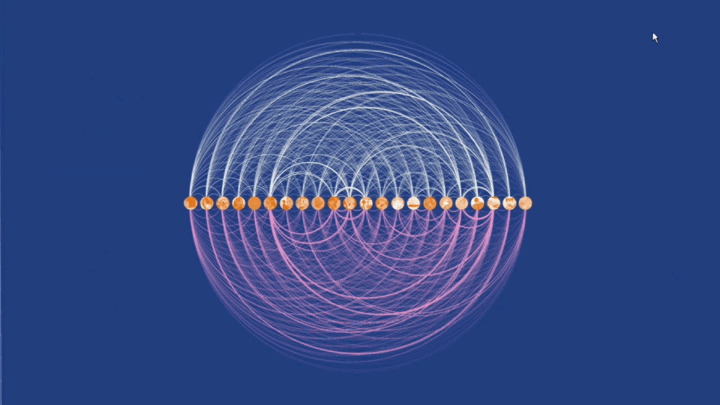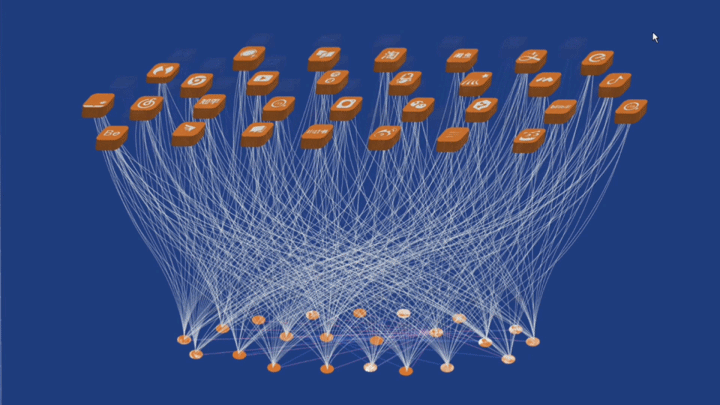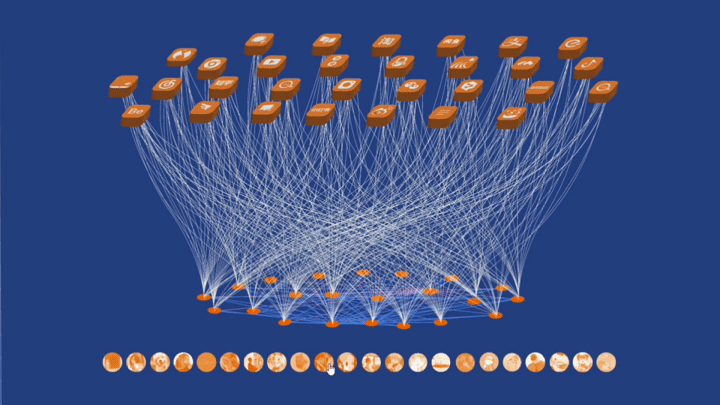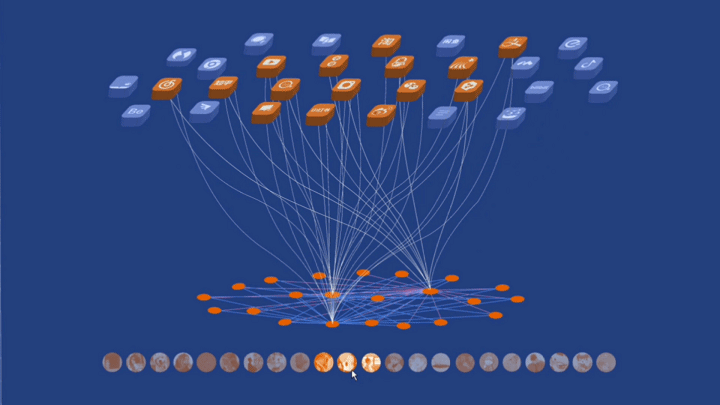
虽然互联网在20世纪50年代才被发明,但”网络”其实早就存在于人类生活的方方面面:蜘蛛编织的用以捕获昆虫的辐射状网络、哺乳动物肺部的血管和肺泡、自然界中的食物链等等。这种在复杂系统中个体和个体的连接,通常称为网络:看得见的、看不见的,形式的、功能的,随机的、秩序的,无向的、有向的。回到今天,网络在可视化中具有重要意义——揭示大规模实体间的关系模式。网络的节点、链接、方向、流量等多个变量在数据的叙事、探索和分析方面都有用武之地。“网络与生活”的3组同学,在认识论的框架下,通过问卷和访谈等形式进行数据收集,呈现了班级内部的分层社交网络、班级同学的梦境故事和流媒体关键意见领袖的内容生产规律。
Although the Internet was invented in the 1950s, "networks" have existed in all aspects of human life: the radial networks spiders weave to catch insects, the blood vessels and alveoli in mammalian lungs, the food chains in nature, and so on. Such connections between individuals in complex systems are often called networks: visible and invisible, formal and functional, random and orderly, undirected and directed. Back to today, networks are of great importance in visualization -- revealing patterns of relationships among large-scale entities. Nodes, links, directions, flows, and many other variables of networks can be utilized for the narrative, exploration, and analysis of data. The three groups of students in "Network and Daily Life" collected data through questionnaires and interviews under epistemological frameworks, presenting hierarchical social networks within the class, dream stories of classmates, and content production patterns of a streaming media producer.